Chemistry is an experimental science, therefore it is necessary to be able to work with units and measurements accurately.
Metric System
The metric system is based on prefixes that indicate a power of 10 with base units.
Metric Prefixes commonly used in chemistry |
Prefix |
Symbol |
Multiple |
Kilo |
k |
1000 |
Deci |
d |
0.1 |
Centi |
c |
0.01 |
Milli |
m |
0.001 |
Micro |
m |
0.000001 |
Nano |
n |
0.000000001 |
SI System
The International System of units gives a standard unit for each type of measurement.
SI Units commonly used in chemistry |
Measurement |
Unit |
Symbol |
Mass |
Kilogram |
kg |
Volume |
Liter |
L |
Temperature |
Kelvin |
K |
Length |
Meters |
m |
Time |
Seconds |
s |
Amount of substance |
Mole |
Mol |
Energy |
Joule |
J |
Charge |
Coulomb |
C |
There are also some important non-SI units as well.
Non-SI Units commonly used in chemistry |
Measurement |
Unit |
Symbol |
Length |
Anstrom |
Å |
Pressure |
Atmosphere |
Atm |
Kilopascal |
kPa |
|
Energy |
Calorie |
cal |
Temperature |
Celcius |
°C |
Taking measurements
Measurements must be taken accurately. Always write down one more decimal place than the instrument tells for certain—a “0” if it’s “one the line” and a “5” if it’s “between the lines.”
Significant Figures
The significant figure rules are to allow people to read data or calculations and know with what precision the data was taken. The significant rules can be summarized in two rules: (1) If a decimal point is not present, count digits starting with the first the first non-zero number and ending with the last non-zero number; (2) If a decimal point is present anywhere in the number, start counting with the first non-zero number and continue until the end of the number. Rules on how to perform calculations with significant figures will be given in a future tutorial.
Fundamental Constants
Several numbers are used throughout chemistry and are important to be familiar with.
Fundamental constants commonly used in chemistry |
Name |
Symbol |
Constant |
Avogadro’s # |
NA |
6.02 X 1023 mol-1 |
Speed of light |
c |
3.0 X 108 m/s |
Gas constant |
R |
8.31 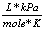 |
|
0.0821 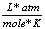 |
Planck’s constant |
h |
6.63 ´ 10-34 J·s |
Charge of electron |
e |
1.6 ´ 10-19 C |
Atomic mass unit |
m |
1.66 ´ 10-24 g |
Std Temp & Pressure |
STP |
273.15 K & 1 atm |
Math skills are needed throughout a chemistry course.
Algebra
Algebra is used to solve equations by un-doing whatever is being done to an unknown variable. For example, if an equation has “x+2” then you would subtract “2” to solve for “x”. Everything that is done to one side must be done to the other side of the equation as well.
Calculations with significant figures
You cannot become more precise after completing calculations than the original data was. Therefore, it is important to write the answer with the correct number of significant figures. When adding and subtracting with significant figures, you write the answer with the least number of decimal places that are in the problem. When multiplying and dividing, write the answer with the least number of significant figures as is in the problems.
Scientific Notation
Scientific notation is a way of writing large or small numbers as a multiple of 10. The decimal place is always placed behind the first non-zero number and the number of times the decimal point was moved to get there is used as the exponent of 10. Positive exponents represent large numbers (>1) and negative exponents represent small numbers (<1).
There are when working with scientific notation numbers:
- Addition with same powers of 10: Add the numbers and keep the power of 10 the same.
- Subtraction with the same powers of 10: Subtract the numbers and keep the power of 10 the same.
- Multiplication: Multiply the numbers and add the powers of 10
- Division: Divide the numbers and subtract the powers of 10
- Power: Take the number to that power and multiply the power of 10 by the power
- Roots: Take the root of the number and divide the power of 10 by the root
Logarithms
Logarithms are a way of counting in multiples of a base number. If 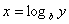 then
then 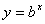 . If no base is specified, it’s assumed to be 10.
. If no base is specified, it’s assumed to be 10.
Calculator Tips
People often get incorrect answers simply from a mistake in the way they enter numbers into their calculator. When dividing by more than one number, use the ¸ button each time. When entering scientific notation, always use the EE (or EXP) button rather than entering (^10). Be sure to use parenthesis around addition and subtraction when combining with multiplication and division, and also when taking a value (especially a negative value) to a power.



