Matrices
| Topic Review on "Title": |
Definition of a matrix:
- Any 2-dimensional array of real or complex numbers.
Square matrix:
- A matrix of type
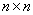 . .
Diagonal:
- The entries of a square matrix in the i-th line and i-th column (same index i), for some i.
Identity matrix:
- A square matrix with 1’s on the diagonal and 0’s off the diagonal.
Zero matrix:
- Any matrix (of any type), with only zero entries.
Definition of a 2-dimensional matrix:
- We define of a 2-dimensional matrix as:
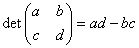 . .
Definition of the rank of a matrix:
- The rank of a matrix A is the greatest n such that A has a square sub-matrix of type nxn with determinant not equal to zero.
Definition of an invertible matrix:
- We say a square matrix A is invertible if there exits a (square) matrix
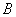 such that such that 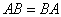 =identity matrix. =identity matrix.
Cramer’s Rule:
- If
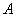 is a square matrix, then the equation is a square matrix, then the equation 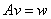 has a unique solution if and only if has a unique solution if and only if 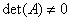 and the solution is and the solution is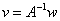 . .
|
| Rapid Study Kit for "Title": |
| Flash Movie |
Flash Game |
Flash Card |
| Core Concept Tutorial |
Problem Solving Drill |
Review Cheat Sheet |
 |
 |
 |
|
| "Title" Tutorial Summary : |
Linear systems can be solved with the use of matrices. Matrix properties and operations facilitated the arrival to solutions with fewer calculations. Some examples show matrix computations and the nature of their solutions.
The idea of Cramer’s rule can be formulated with the use of matrices. Cramer’s rule is a famous rule that uses determinants to finding solutions to a system of equations. The addition or multiplication of rows and columns in a matrix allow matrices to be reduced.
|
| Tutorial Features: |
Specific Tutorial Features:
• Matrix operations are shown in some of the examples.
• Matrix computations are presented in the examples.
• Step by step explanation of the rank of a matrix with respect to a determinant is shown in a couple of examples.
Series Features:
• Concept map showing inter-connections of new concepts in this tutorial and those previously introduced.
• Definition slides introduce terms as they are needed.
• Visual representation of concepts
• Animated examples—worked out step by step
• A concise summary is given at the conclusion of the tutorial.
|
| "Title" Topic List: |
The definition of matrices
Matrices
The sum and product of matrices
Determinants
Matrices that are two dimensional
Matrices that are three dimensional
A rank of a matrix
Linear systems and the rank of a matrix
Matrix Inverse
Definition of the inverse of a matrix
Cramer’s Rule
Matrix Reduction
Definition of equivalent matrices |
See all 24 lessons in High School Algebra 2, including concept tutorials, problem drills and cheat sheets:
Teach Yourself High School Algebra 2 Visually in 24 Hours |



